Network Structure and Group Influences in Social Media
Community Structure
Social networks are about community. The collective participation of members; collectively creating value.
Community
A unified body of individuals, unified by interests, location, occupation, common history, or political and economic concerns.
Online communities
A group of people who come together for a specific purpose, who are guided by community policies, and who are supported by an online vehicle or host that enables virtual communication among members. A cyberplace where people connect online with kindred spirits, engage in supportive and sociable relationships with them, and imbue their activity online with meaning, belonging and identity.
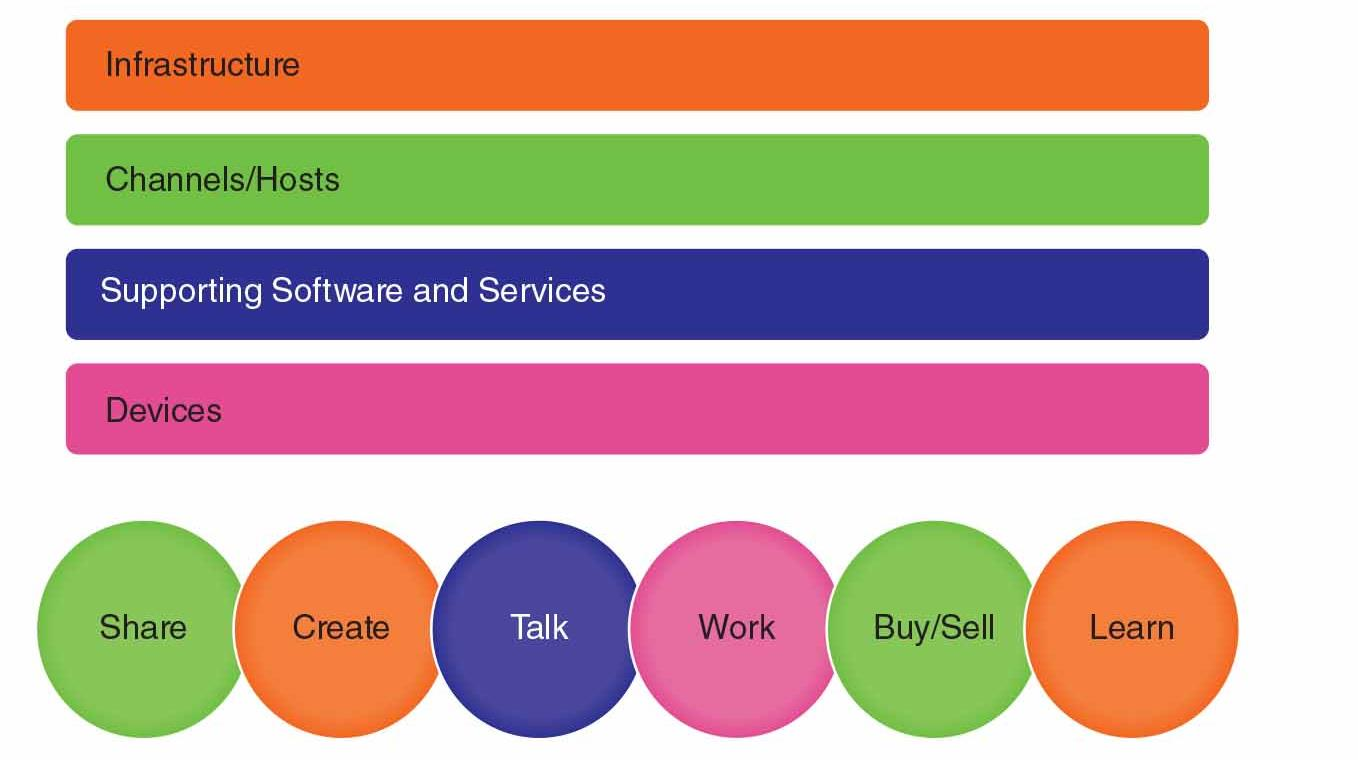
Social Media Value Chain
The core activities of social media participants and the components that make those activities possible.
Brand Communities
Three markers exist for a brand community:
- Shared consciousness (they feel like family to each other, like to distinguish from rival communities)
- Rituals and traditions (often symbolic practices aimed at preserving meanings, history of brand and identity)
- Obligations to society (concern for welfare of fellow members of the brand, often providing assistance to each other on behalf of the brand)
Muniz, A. M., & O'guinn, T. C. (2001). Brand community. Journal of Consumer Research, 27(4), 412-432.
Networks
- All social media is networked. All social communities are networks of social networks.
- The network effect: the relative value a community offers its members is tied to its membership; it gains additional value as more people use it.
- Social network theory: social relationships comprise nodes and ties.
The Vocabulary of Networks
- Nodes: Members of a network. Can be people, organisations, articles, countries, departments, or other definable units..
- Network Units: Another term for nodes – members of a network.Members are connected by their relationships or ties.Relationships can be in the form of friends, fans, links, contacts and more.
- Interactions: Behaviour-based ties experienced by connected nodes.
- Flows: Interactions create flows among connected members. When flows go in many directions and on multiple platforms, this is called media multiplexity.
Social Networks
Social network: A set of socially relevant nodes connected by one or more relations. Social network sites networked communication platforms in which participants:
- Have uniquely identifiable profiles that consist of user-supplied content, content provided by other users, and/or system-provided data
- Can publicly articulate connection that can be viewed and transversed by others
- Can consumer, produce and/or interact with streams of user-generated content provided by their connections on the site
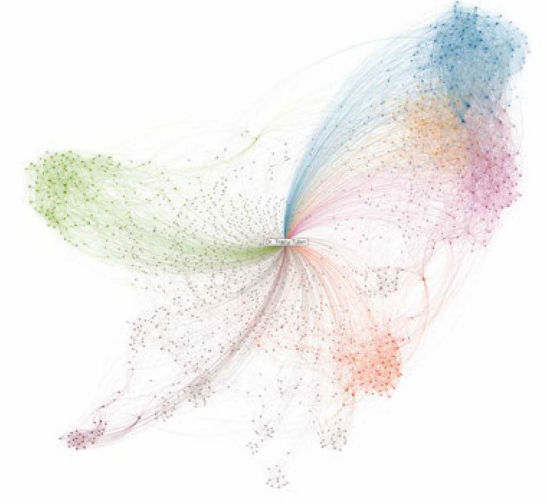
A LinkedIn Network Map Visualization
- The circles represent nodes (LinkedIn members)
- The lines between (connections) represent ties
- Information about degrees of separation is also available
Six Degrees of Separation
Six degrees of separation is an observation that everyone is connected to everyone else by no more than six ties. 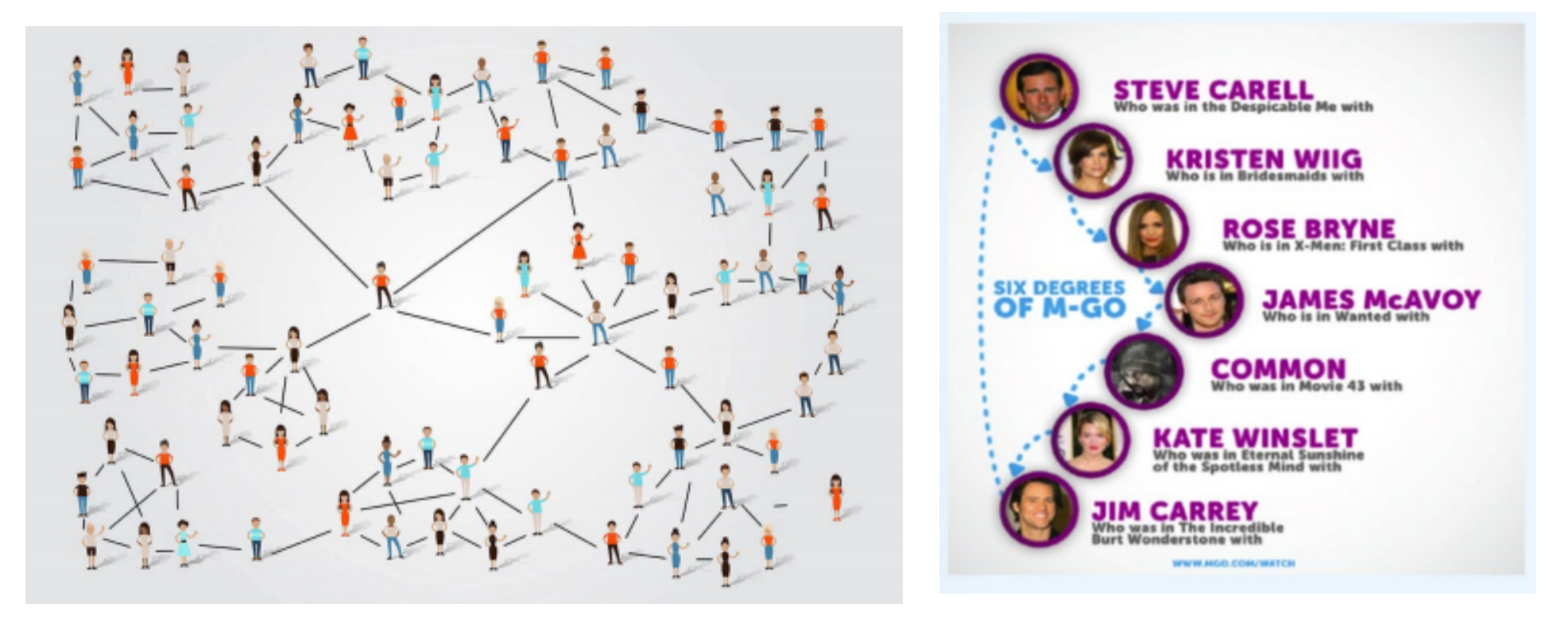
📺 [Six Degrees Video](http://you tu.be/a99ry70CnRs) https://www.sixdegrees.org/
Characteristics of Online Communities
All communities (online or physical) share important characteristics: a feeling of membership, a sense of proximity to one another, and some level of interest in the community’s activities. Social networks provide members with a location and the functionality to connect, communicate and collaborate. 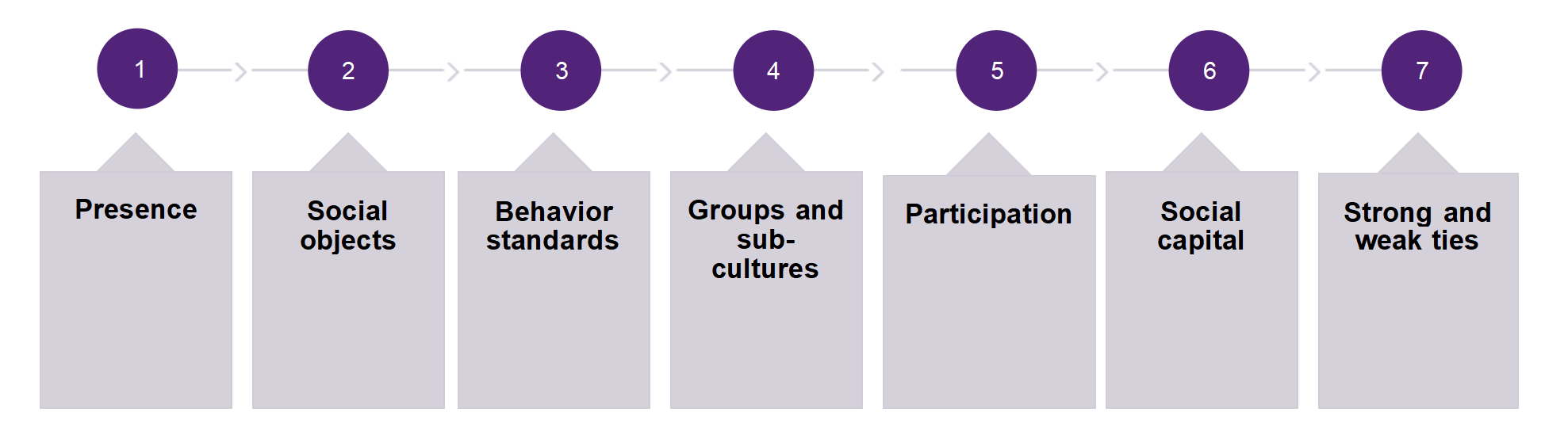
Presence
- The effect that people experience when they interact with a computer-mediated or computer-generated environment.
- Sense of presence is enhanced through social media when the environment looks and/or feels real.
Purposive Value and Social Objects
- Social networks need commonalities to create bonds among members.
- They provide spaces for content to be generated, shared, consumed,fortified and promoted by community members. Content can be dialogue,shared writings, photos and more. The content can be seen as an object when it is a thing of common interest.
- Objects, things of common interest, have the primary function of mediating interactions between people. All relationships have** social objects embedded** in them.
Social object theory: Social networks will be more effective if there is a way to activate relationships among people and objects. Shared objects give meaning to social a vehicle and motivate member engagement.
Object sociality: the extent to which users can share an object in social media; related to an audience’s unique interests.
Behaviour Standards
Virtual communities need norms and rules that govern behaviour. Members learn norms and rules through socialisation.
- Flaming: Posts written with all capital letters to express anger
- Doxing: Identifying and publishing private information about someone as a form of punishment or revenge.
- Trolling: Deliberate provocation of conflict by posting messages that are inflammatory, controversial, insulting and/or provocative.
- Cyberbullying: The use of digital technologies with an intent to offend, humiliate, threaten, harass or abuse somebody.
Groups and Subcultures
Social media enables groups and subcultures to network and collaborate.Members affiliate with communities they identify with. Social identity is the part of the individual's self-concept that is related to group membership, and helps explain participation in social communities.
- Crowdcultures: When online communities get together and share a cultural perspective, forming subcultures around different topics.
- Crowdsourcing: When tasks are completed collaboratively by a large group of
- people such that the resulting value far exceeds that which could have been contributed by a single participant.
- Intentional: social action Participation but in the context of a group; influenced by individual attitudes and characteristics and the context and norms of the group.
Participation For an online community to thrive, a significant proportion of its members must participate.
There are four elements of social site participation:
- People with whom you are connected
- The content (artefacts) produced on the site
- The feedback received from others
- The distribution of artefacts and feedback throughout the network
Participation fuels engagement. Engagement is a psychological state that occurs through interactive, co-creative consumer experiences with a focal agent/object.
Social Capital
Social capital: Accumulated resources that can be ‘traded’ for other things. The resource may be actual or virtual and may be held by an individual or group. Communities can build capital through reputation and structure.
- Bridging: Value from others who provide access to places, people, or ideas that one may not be able to get on their own.
- Bonding: Value in the form of emotional support
- Maintained: Value from maintaining friendships with latent ties.
Strong and Weak Ties
Members of online communities may accrue resources easily as they have accessibility to people who can help with a variety of issues; even if they may not know them personally.
- Core ties: Connections with whom one has a very strong relationship
- Significant ties: Somewhat close ties, but less close than core ties
- Weak ties: Connections based on superficial experiences or very few connections
- Latent ties: Pre-existing connections that have been discarded.
Flow and the Influence Network
Two-step flow of communication: Ideas flow from the source (e.g. radio or print) to opinion leaders and from them to the less active sections of the population.
It is now thought of more as a two-way dialogue as people communicate information to one another and with the opinion leader in an influence network.
A piece of information can trigger a sequence of interactions (Figure). 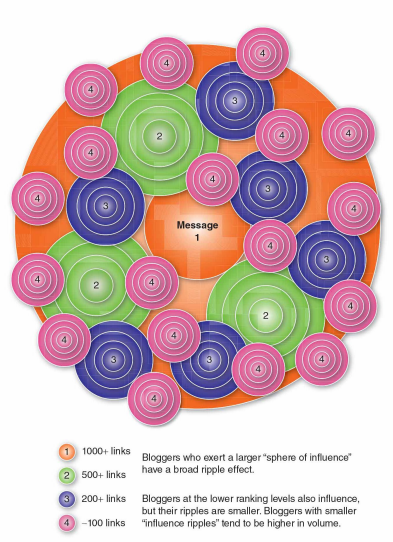
Viral Content and Memes
Viral content: Content a large number of people in one or more social communities deemed relevant, valuable or as needing to be shared.
Community member then influence the spread of the content by sharing it with their own social networks.
When viral content evolves, it becomes a meme.
Meme: A snippet of cultural information that spreads from person to person until it enters the general consciousness.

Spreading Viral Content
Mass connectors: About 6.2% of social media users are responsible for about 80% of the impressions. Impressions refer to a view or exposed to an advertising message.
- There are three types of people that can help to spread viral messages:
- Mavens are people who are knowledgeable about many things.
- Connectors are people who know many people and communicate with them.
- Salespeople are people who influence others with their natural persuasive power.
If an idea is sticky it has memorable impact and stays with us for a long time
Ideas spread more easily when conditions are right*
Internet Trolling
Trolling: Deliberate provocation of conflict by posting messages that are inflammatory,controversial, insulting and/or provocative.
Social Media Trolls: who purposely says something controversial in order to get a rise out of other users.
Being online often means managing trolls
https://www.eminentseo.com/blog/ballers-guide-managing-social-media-trolls/
Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying: the use of digital technologies with an intent to offend, humiliate, threaten, harass or abuse somebody.
- Nasty messages online or on your mobile phone
- Comments or replies on your social media posts or posts about you
- Being excluded from online group chats on purpose
- Embarrassing or harmful photos being put online without your permission
- Sending offensive pictures through a messaging app
- Rumours and lies about you on a website, messaging app or social media platform
- Offensive chat or voice communication on an online game
- Fake online profiles being created with an intent to defame you
Cyberbullying Statistics
- Post about politics are most likely to receive bullying remarks, followed by sport and food
- Cyberbullying on Twitter is most prevalent on Sundays and between 6 pm and 8 pm
- The majority of insults on Twitter related to intelligence (33%) and appearance (20%)
- Female trolls tend to attack the victim's intelligence (dumb, stupid) or appearance (fat, ugly), while males were more likely to use homophobic insults.
Influencers
Influencers (also known as opinion leaders or power users) are people that others view as knowledgeable sources of information.
Five characteristics:
- Activists
- Connected
- Impact
- Active minds
- Trendsetters
Influencer Types
Based on follower numbers:
- Nano influencers: 1k-5k followers
- Micro influencers: 5k-50k followers
- Macro influencers: 50k-500k followers
- Mega influencers: >500k followers